BSBESB301 – Investigate Business Opportunities
In this unit you will learn how to;
- Identify potential opportunities for business
- Investigate market needs and factors affecting the market
- Finalise the investigation into business opportunities
Introduction
Why do you need to look for business opportunities? People come into your shop of office to do business; they will either buy what you are offering – or they won’t. Simple right?
Not right; a successful business is one that does not rely on customers simply walking in the door. A successful business is one that makes every effort to identify ways of improving their customer service levels, the products and services they offer and, above all, increasing their income.
They do this by seeking out business opportunities.
Competing in the world of business
The idea for a business opportunity might come in a flash of creative inspiration, but the success of this idea will rest on hard work and a thorough knowledge of the business environment in which you operate.
To put the nature of the business world into perspective, and to understand why it is important to identify areas and opportunities for improvement; consider the relationship between businesses, and industries, and how they revolve around a customer’s disposable income. Disposable income is what you have left after paying your bills, such as mortgage or rent, utilities, and buying essential items such as food.
Customers buy because they have a need or desire. When considering how to spend their money these needs and desires will affect their choice; they may consider what is practical or most necessary at the time (a needs based choice) or what will make them feel happy (a desire based choice). They may choose to make home improvements, buy furniture, put their money into a savings account, buy a new car or take a long holiday. Whatever the reason for that choice, each industry, shown in the pie below, will be chasing the same customer dollar as you; they are in indirect competition with you.
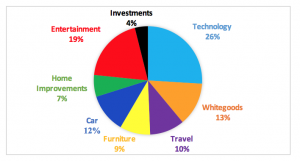
The chart is an example of the types of things a consumer might spend their disposable income on.
All the industries shown, and many more, are competing for a slice of this pie and it should be the aim of every successful organisation to earn their share.
Your direct competitors come from within your own slice of the pie. For example, the travel slice is made up of several travel industry sectors such as;
- transportation which is made up of airlines, coaches, rail, car hire and cruises
- accommodation, which includes hotels, motels, resorts, bed and breakfast and so on
- tourist attractions such as theme parks, museums, animal parks etc.
… just to name a few. These sectors, in turn, can be broken down even further. The airline sector, for example, can be broken down to individual companies; Qantas, Singapore Airlines, Lufthansa German Airlines, British Airways and so on, all of whom are actively promoting themselves to potential customers.
Direct competition (within your own industry / sector)
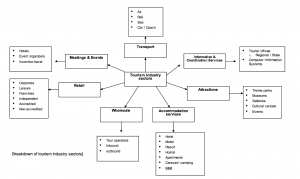
So in addition to competing indirectly with other industries for a share of the disposable income pie, you also have to compete within your own industry and within your own sector to win a customer’s business. Identifying business opportunities, then, is a matter of necessity if a business is to grow and remain successful.
In identifying opportunities, in brief, you begin with a sound understanding of your own organisation, its products and services and the industry to which you belong; looking at what you could, potentially, offer or change to gain new business. Having established what you could offer, it then becomes a matter of researching the market; what are the current trends and developments in the market in which you operate, how do these relate to what your organisation does, who might your target audience be – and identifying business opportunities open to you. We will look at all of these aspects as we move through the unit.
Identifying potential opportunities for your business
Finding ways of improving your customer service and maximizing your income is an ongoing and essential element in the continuous improvement process in any successful business.
But how do you go about identifying the opportunities to do so?
In the initial instance you pay attention to what your organisation actually has to offer, and gain a full understanding of your industry; who it’s customers are, what their current needs seem to be, what your organisation has to offer. This understanding will give you a foundation upon which to build sound choices.
Sourcing and analysing market information for potential opportunities
Knowledge of your own organisation will form only part of the picture you need to identify opportunities and move forward. There are a number of useful information sources that can help identify ideas and potential opportunities. These can include (but are not limited to);
- chambers of commerce – who have insights into local business issues in a range of different industries and organisations and may be able to point out local opportunities, developments and trends that you could take advantage of. They can also help you network with useful people, and provide referrals to other organisations that can be helpful to you.
- government business information services – these could be federal, state and/or local and can provide you with useful statistical data as well as information on regulatory and legislative requirements that might impact on your business or industry.
- public reports – are often produced by government or industry bodies that provide information on latest trends, economic outlooks, any research being done in areas of interest to your organisation and much more.
- internet research – the internet is a limitless source of information. It should be noted, however, that not all information sourced on the internet will be accurate or true; anyone can post their views on blogs, social media platforms or on their own websites without, necessarily, having the knowledge or expertise to make sound judgements. Care should therefore be taken about which sites you use to gather information. When used efficiently, however, the internet can provide useful information on what products and service are currently in demand.
- newspapers – can be an excellent source of inspiration. Stories about new housing developments mean that the population in a given area will be increasing (for example), meaning access to more customers. Stories about a major competitor planning a move into your area of operation can give you the time and opportunity to develop strategies and identify opportunities to cement your stake in the local area – before the competitor arrives. These are only a couple of examples of how an awareness of local news can help you identify opportunities.
- peak industry bodies – can provide expert opinions and a deep down insight into the opportunities that exist within that industry. Examples of peak industry bodies are;
- experience by users or employees – customers who have used your products as well as employees of your organisation can often have valuable information on how these products work in a real world sense. They can often give you insight into how they could be improved.
- competitor activities, products and services – knowing what your competitors are doing, and what they are offering, is an essential component in business operations. You need to be aware of what differentiates you from them and how you can take advantage of, and heighten, these differences. Such information can also help you counteract any negative impact their activities might have on your organisation.
- industry trends and insights – this is another important business area; in order to improve your business and identify opportunities to do so, you must be aware of what customers are interested in and any new emerging trends. We will look at this subject in more detail in the next section.
This represents a substantial list of source information, but what is it, exactly, that you need to look for? Most (if not all) businesses exist to make money. They do this by offering products and services that consumers want, or need, to buy. So in recognizing a potential business opportunity you first need to know such things as what consumers are interested in, where they are located, how this might relate back to your organisation’s current offerings, and what you might need to do to take advantage of that interest. Information such as this can be found by researching;
- new and emerging markets and their features. Emerging markets are countries that are transitioning from a “development” phase to a “developed” one, so the term Emerging Markets refers to an economy that is experiencing considerable growth. Such countries have common features including;
- Market volatility; this generally stems from political instability, external price movement and supply demand shocks (due to natural disasters). This exposes investors to the risk of exchange rate fluctuations as well as market performance.
- Growth and investment potential. Emerging markets are often attractive to foreign investors due to the high return on their investment. Labour and material costs in such countries are often much lower than in our own, so using this advantage they can focus on exporting low cost goods to richer nations which, in turn, boosts their GDP growth, stock prices and returns for investors.
- High rates of economic growth; governments of emerging markets tend to implement policies in favour on industrialization and rapid economic growth. These policies lead to lower unemployment, better living conditions, higher disposable income for local workers, higher investments and better infrastructure.
- Income per capita; emerging markets often have a low-middle income per capita compared to other countries. As the economies grow, the income per capita increases.
At present, the five major emerging markets are Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. Why is this important information?
With more and more people buying online than ever before, your customer base is no longer restricted to your neighbourhood – it has expanded to, potentially, encompass the entire world.
So it is important to understand where emerging markets, who now have money to spend, can be found and the opportunities they represent; how they relate to your organisation and what you might have to offer them.
For more information, see;
https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/economics/emerging-markets
- expected market growth or decline and associated risk factors. This type of information is vital. There is, for example, no point in investing significant time, money and effort into a project if the economic climate and/or the market for your product is currently in decline. Growth or decline statistics (which are often available from government departments or industry bodies) can provide you with the ability to make correct decisions based on known facts. Market growth can mean improved access to customers and their disposable income; so investing funds and effort are less of a risk. A market in decline on the other hand might mean a potential loss of business.; a risk that you need to plan for. Either way, having this information means you can identify opportunities to improve or adjust your business operations accordingly.
- economic activity, including projected or potential movements in prices. The state of the economy, both national and international, plays an essential part in your considerations. The economy is in a constant state of flux;
- Interest rates and employment rates are constantly changing, making it difficult to predict what the market will do.
- Population growth and immigration put pressure on resource availability
- Movements in pricing can have a significant impact on the market.Price movements in a market such as Australia can be volatile due to our reliance on imported goods and other foreign trade issues that are subject to currency fluctuations which, in turn, can impact on pricing; the ever changing fuel prices are a prime example of this and it is a cost consideration when evaluating your ideas.
- projected changes in availability of resources. Whatever business you are in you will need access to resources. Resource management is a fundamental role in the efficient functioning of any business; knowing which resources are available at any given time is an important factor in deciding how to distribute and allocate the right assets for any given project or task. The last few years have seen the extraordinary impact that worldwide crises, such as global pandemics and aggressive actions against other countries, can have on the availability of some resources, as we experience shortages in everyday household products, delivery systems, energy and fuel products. Then, too, new consumer trends can create a sudden, unexpected, demand for the resources you need to provide your products and services to customers, leading to shortages which, then, impact on the organisation’s ability to function efficiently.
Analysing the information gathered
Having gathered a, potentially large, range of information you will need to determine what might lead to actual opportunities relevant to your your business. To avoid confusion and becoming overwhelmed by a mass of information you should sort through and analyse this initial research by listing the details of business ideas and opportunities.
Putting the ideas down in writing allows you to apply a logical flow to the information, clarifying each opportunity and answering specific questions some of which might be;
- What is the value of this particular opportunity or idea?
- What are the benefits of the idea?
- How does this it fit in with our current operation and processes?
- Do we have the capacity and capability to implement the idea?
- How does it fit into our organisational culture and mission?
- What resources will we need to develop and implement the idea?
- Will we need to find investors or seek funding?
- Is anyone else doing this? If so; who?
- Is the demand for this idea large enough to warrant expense and resource usage?
- What risks might we face in implementing this idea?
Analysing and answering these questions will let you determine which of these ideas could potentially work.
…. continued in the learner guide ….
For purchase information go to business page.
